Following the recent publication of AIRINC’s Global Tax Rates Maps, which provide a visual representation of effective tax rates around the world, we’re excited to focus on the United States in this installment of our blog series. In this series, we explored the diverse tax landscapes from Europe and the Middle East through Africa and APAC. Now, we turn our attention to the unique complexities of the US tax system.
The US Tax Rates Map Explained
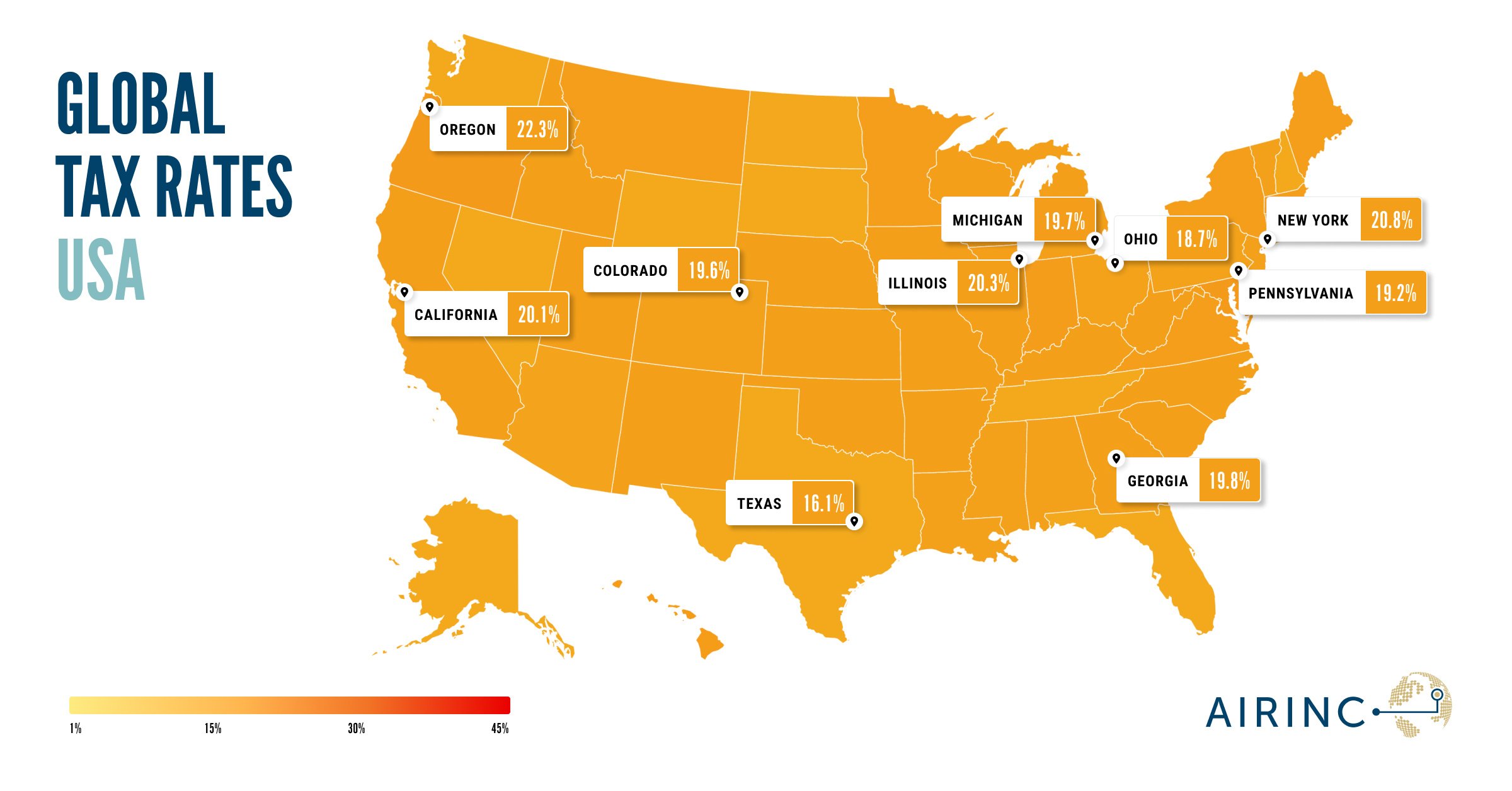
The US tax Rates map provides a striking visual of how federal and state taxes interact. Middle-income earners in high-tax states like California and New York see significant portions of their income go to taxes, while no-tax states like Texas and Florida offer more take-home pay. For global mobility programs, the map is an essential tool for planning assignments and understanding regional tax burdens. Tax burdens generally in the United States are moderate compared to other developed countries – the effective tax rate for middle-income taxpayers ranges from 16% to 21% depending that varies by state.
Why the US Tax Map Is Relevant for Mobility
- State-by-State Variations: The Rates map clearly shows how state taxes can drastically alter an assignee’s financial situation. High-tax states may require additional allowances to maintain net income, with California and New York assessing the highest tax rates. In contrast, there are nine states that do not assess income tax on employment income, including Florida and Texas. In those no-tax states, revenues are generally funded through other means, including property taxes and sales taxes.
- Child Tax Credits and Deductions: The map emphasizes the importance of federal tax breaks for families, which can significantly reduce effective tax rates. This includes the child tax credit of $2,000 per child. Under the expanded standard deduction available to individuals under existing tax law, fewer and fewer taxpayers are claiming itemized deductions for mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and state and local taxes. According to the IRS, only about 10% of U.S. taxpayers still itemize since the standard deduction provides a lower tax liability.
- Social Security Implications: The capped social security system highlighted on the map affects middle-income earners more than higher earners as the FICA contribution of 6.2% is capped to wages up to $176,100. Mobility teams should consider these nuances when structuring compensation.
Upcoming Tax Changes in the US
- Reconciliation Bill enacted July 4, 2025 – the One Big Beautiful Bill Act “OBBBA”: The bill makes many existing tax provisions permanent — including the 37% top marginal rate, expanded standard deductions, and an expanded cap on SALT deductions. Moving expenses remain non-deductible permanently under the OBBBA and the enhanced child tax credit will generally remain in place. There are also temporary incentives like deductions for tips and premium overtime pay (but these remain subject to FICA and Medicare), a deduction for car loan interest, and a new deduction for seniors over age 65. These temporary provisions would only last four years. The legislation introduces several key changes that impact individuals and are effective retroactively for 2025:
- Enhanced standard deductions – For a married taxpayer filing jointly, the standard deduction has been enhanced from $30,000 to $31,500. Other filing status taxpayers will have similar enhanced standard deductions.
- Enhanced SALT deduction – The state and local tax deduction cap increased from $10,000 to $40,000 for married taxpayers filing jointly with incomes up to $500,000. The extra $30,000 SALT cap is phased out for incomes exceeding the threshold.
- Enhanced child tax credit (CTC) – The CTC for qualifying children under age 17 has been enhanced from $2,000 per child to $2,200.
We are in the process of updating our 2025 AIRINC US tax data for these OBBBA changes. Other provisions of the OBBBA impacting individuals will be effective for 2026, including phaseouts of itemized deductions for higher incomes, a floor for charitable contributions, a charity deduction for taxpayers that do not itemize, and revised AMT thresholds.
- State-Level Tax Reforms: Several states have been implementing tax changes recently – generally tax cuts that are phased in gradually over several years – as improving state budgets allow for returning surplus revenues to taxpayers. For instance, some states are moving towards flat tax rates, while others are eliminating taxes on earned income altogether. As the implications of the federal budget funding are better understood, it is possible that states may need to revisit their budgets and tax revenues.
Why Choose AIRINC?
AIRINC’s tax solutions are designed to address the multifaceted challenges of global mobility programs. Their combination of accurate data, strategic insights, and tailored advisory services empowers organizations to manage costs, ensure compliance, and maintain employee satisfaction. Whether dealing with tax equalization, planning assignments, or adapting to tax law changes, AIRINC delivers the expertise and tools to succeed in a globalized world.
Want to hear even more on tax?!
Want to be the first to hear about all our tax news? Subscribe to the blog for updates, including details on our upcoming Summer Tax School in collaboration with the Global Tax Network. You won’t want to miss it! Subscribe here.
Are you looking for information on global tax rates around the world?AIRINC’s International Tax Guide contains all of the information you need to support your assignment tax planning — including global tax rates, deductions, and employee/employer social security contributions. |
Are you trying to move an employee from a lower- to a higher-tax rate location?Use AIRINC’s Global Salary Comparison to understand the compensation you would need to offer to cover the difference and make the appropriate offer to your employee. |
Join us for more on tax!Starting this month, we’re teaming up with our friends at Global Tax Network (GTN) to bring you a three-part summer webinar series focused on the ins and outs of global mobility taxation. First up Mobility Tax 101 - Foundations of Global Mobility Taxation. Join us to learn the fundamentals of international mobility taxation - register here. |




%20(31).png)

