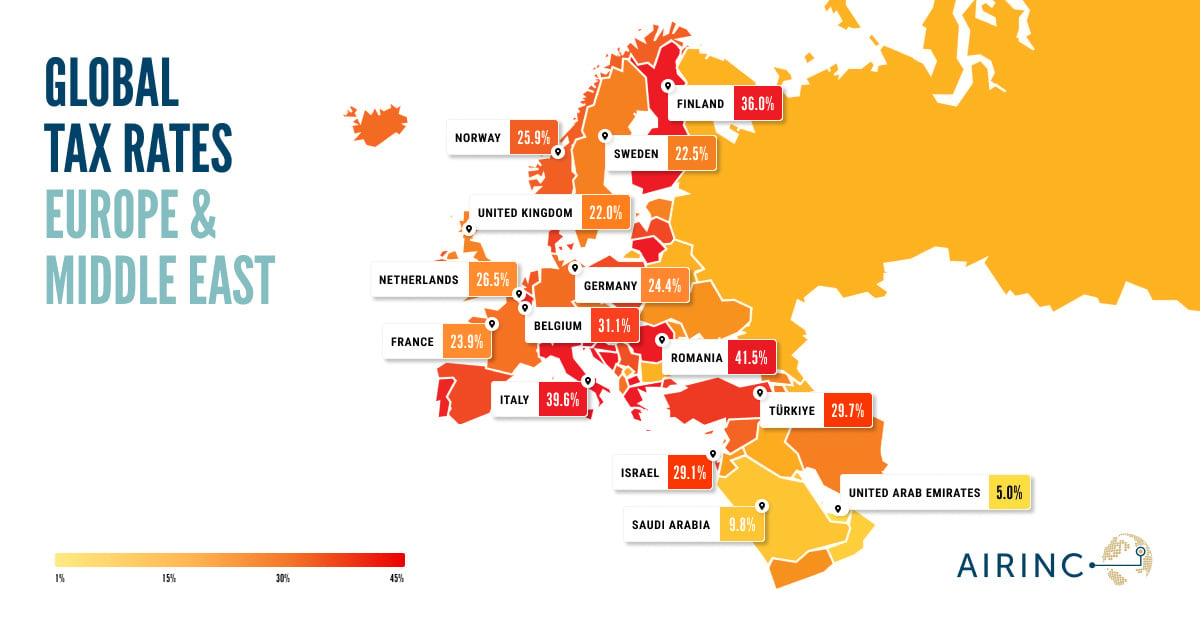
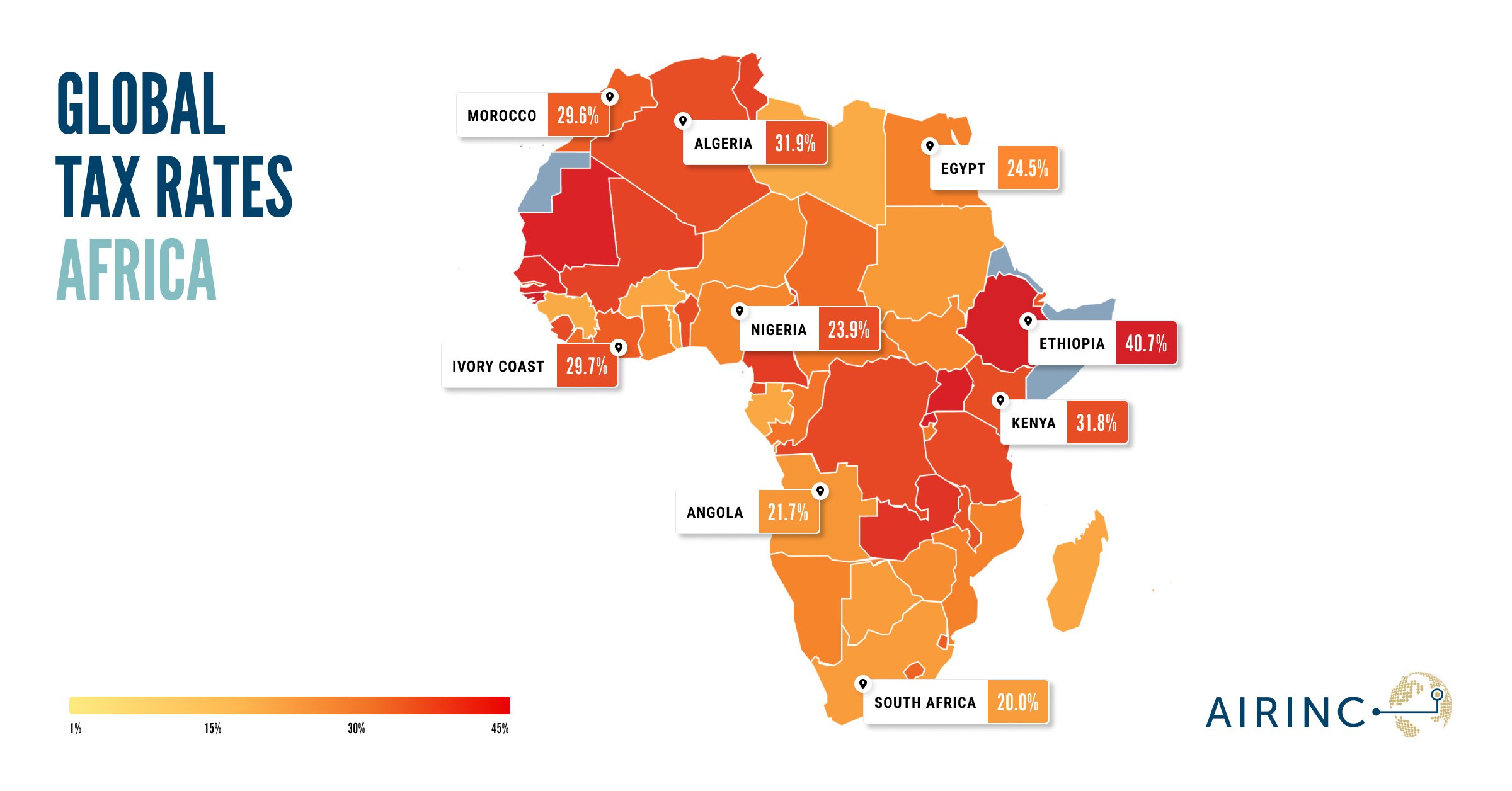
Tax regulations are evolving worldwide, with significant changes affecting expatriates in Cuba, Jersey, Ukraine, and Sierra Leone. Understanding these updates is essential for effective financial planning and compliance. These changes can have far-reaching impacts on expatriates and their organizations, requiring careful attention to detail
AIRINC’s Data Points page delivers the latest insights on global mobility, cost-of-living trends, and economic shifts including tax. This blog update focuses on key tax changes, using fresh data from Data Points to highlight how these updates impact international employees and businesses. Published every quarter, this resource helps organizations stay ahead of evolving tax policies and global compensation trends.
Key Updates:
Cuba:
Pictured
Income tax rates have surged, with the top rate reverting to 50%, creating a substantial impact on expatriate earnings. This shift reflects the government’s efforts to boost public revenues but places additional financial pressure on taxpayers. Employers may need to adjust compensation packages to offset the higher tax burden.
Jersey:
Independent taxation for married couples will be mandatory by 2025. Other changes include increased personal exemptions and adjustments to social security contributions, varying impacts based on income and family size. These reforms aim to modernize the tax system, but they also introduce complexities that expatriates must navigate carefully.
Ukraine:
To fund the ongoing war effort, the military levy has increased to 5%, bringing the total flat tax rate to 23%. Employer-funded social security contributions remain a significant cost. Companies operating in Ukraine need to evaluate the financial implications of these changes on their workforce and ensure compliance with updated regulations. Martial Law has again been extended to at least May 9, 2025.
Sierra Leone:
The redenomination of the currency from SLL to SLE (known as the Leone) aims to curb inflation and stabilize the economy, with updated tax schedules reflecting the transition. While the redenomination simplifies financial transactions, expatriates may still face challenges adapting to the new currency framework and managing its impact on their purchasing power.
Conclusion:
Adapting to tax changes is crucial for managing expatriate assignments effectively. Companies must review their policies to ensure compliance and mitigate financial burdens on employees. Collaboration with tax advisors can provide valuable insights and help streamline the adjustment process.
Income tax is often the largest cost item in an international assignment!
An accurate determination of hypothetical and gross-up taxes is essential to the design of equitable expatriate compensation packages. It is particularly important to determine employees’ contributions to their worldwide tax obligations. The AIRINC in-house tax team keep up-to-date so you can stay compliant with ever-changing tax laws. If you need international tax data contact us. We are always happy to talk tax!





%20(28).png)